Introduction
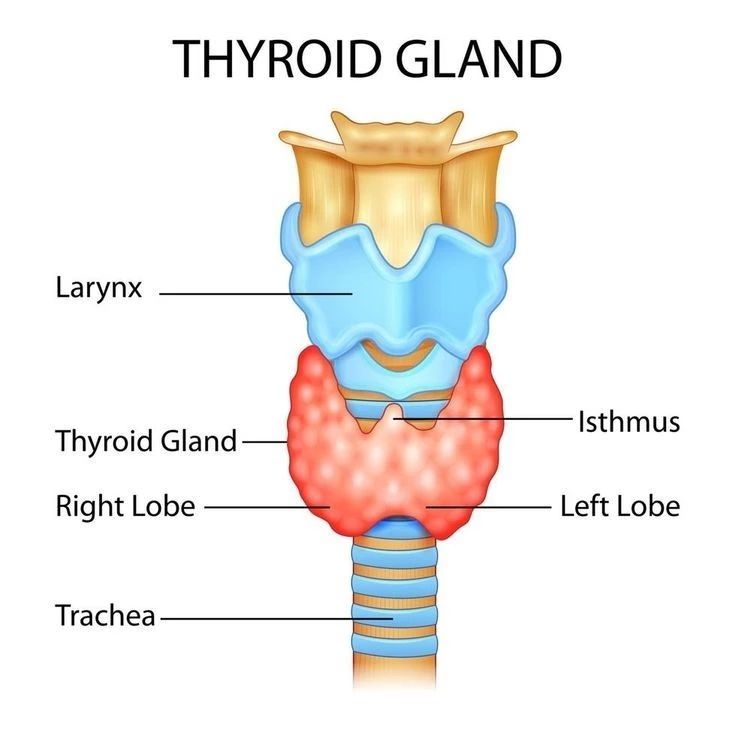
The thyroid gland plays a vital role in metabolism, energy regulation, and growth. Understanding thyroid hormone physiology is crucial for diagnosing conditions like hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism.
Thyroid Hormones & Their Functions
- T3 (Triiodothyronine) – Active form of thyroid hormone, increases metabolism.
- T4 (Thyroxine) – Precursor to T3, maintains metabolic stability.
- Calcitonin – Regulates calcium homeostasis.
Thyroid Disorders
-
Hypothyroidism
- Causes: Iodine deficiency, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
- Symptoms: Fatigue, weight gain, bradycardia, cold intolerance.
- Treatment: Levothyroxine (T4 replacement therapy).
-
Hyperthyroidism
- Causes: Grave’s disease, toxic multinodular goiter.
- Symptoms: Weight loss, tachycardia, heat intolerance, exophthalmos.
- Treatment: Antithyroid drugs (Methimazole, Propylthiouracil), radioactive iodine therapy.
-
Thyroid Neoplasms
- Types: Papillary, follicular, medullary, and anaplastic thyroid cancer.
Conclusion
Thyroid disorders are among the most common endocrine diseases. These MBBS notes provide an in-depth guide for diagnosis and treatment strategies.