Introduction
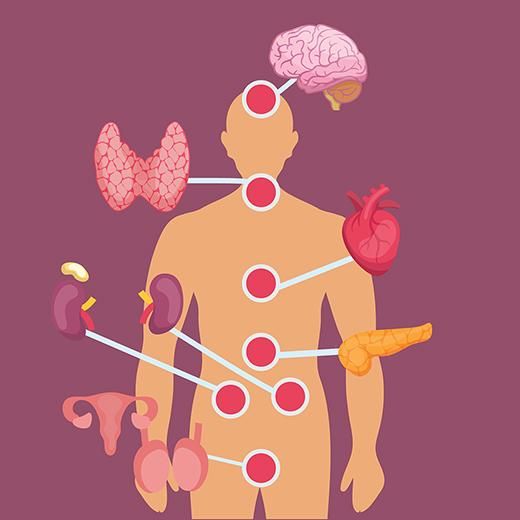
The endocrine system maintains hormonal balance through feedback mechanisms that regulate secretion based on physiological needs. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for diagnosing endocrine disorders.
Types of Hormonal Feedback
-
Negative Feedback (Most Common)
- Hormone secretion is inhibited when levels reach an optimal range.
-
Example:
-
Thyroid Hormone Regulation:
- High T3/T4 → Inhibits TRH (hypothalamus) & TSH (pituitary) → Decreases T3/T4 production.
-
Thyroid Hormone Regulation:
-
Positive Feedback (Rare, Amplifies Response)
- Hormone secretion is enhanced to intensify physiological effects.
-
Example:
- Oxytocin in Labor: Uterine contractions → More oxytocin → Stronger contractions → Birth.
Clinical Relevance
- Defective feedback leads to hormone imbalances (e.g., Cushing’s syndrome, Thyroid disorders).
- Dexamethasone suppression test helps diagnose Cushing’s syndrome.
Conclusion
Hormonal feedback mechanisms maintain homeostasis and prevent endocrine dysfunction. These MBBS notes provide a structured understanding of regulatory pathways.