Introduction
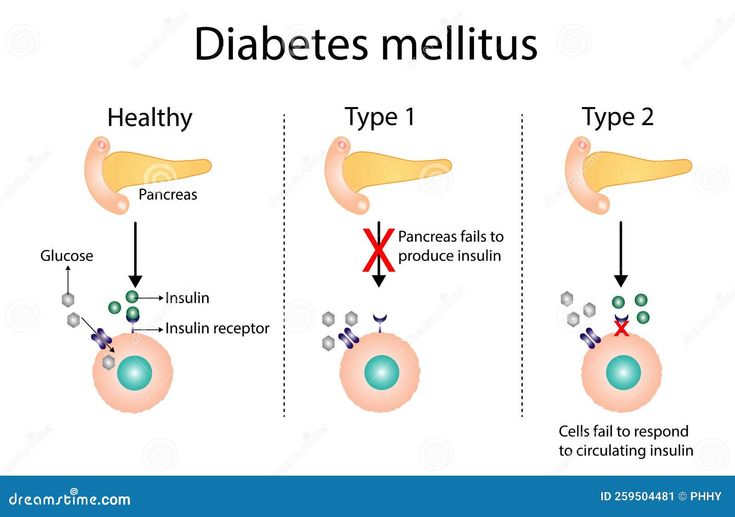
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by hyperglycemia due to defects in insulin secretion, action, or both. It is one of the most important topics in endocrinology and a critical part of MBBS notes for medical students preparing for NEET PG and USMLE.
Types of Diabetes Mellitus
-
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM)
- Autoimmune destruction of pancreatic beta cells → Insulin deficiency.
- Occurs in children and young adults.
- Requires lifelong insulin therapy.
-
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM)
- Characterized by insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency.
- Strongly associated with obesity, sedentary lifestyle, and genetics.
- Treated with oral hypoglycemics (Metformin, SGLT2 inhibitors, GLP-1 analogs) and lifestyle modifications.
-
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM)
- Glucose intolerance first diagnosed during pregnancy.
- Increases risk of Type 2 diabetes postpartum.
- Managed with diet, exercise, and insulin if needed.
Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus
- Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG): ≥126 mg/dL.
- 2-hour OGTT (Oral Glucose Tolerance Test): ≥200 mg/dL.
- HbA1c (Glycated Hemoglobin): ≥6.5%.
- Random Plasma Glucose: ≥200 mg/dL + symptoms.
Complications of Diabetes
- Acute: Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA), Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State (HHS).
- Chronic: Retinopathy, Nephropathy, Neuropathy, Cardiovascular disease.
Management
- Lifestyle modifications: Diet, weight loss, and exercise.
- Medications: Oral hypoglycemics, insulin therapy.
- Regular monitoring: HbA1c every 3 months.
Conclusion
Diabetes mellitus is a lifelong condition requiring early diagnosis and strict glycemic control. These MBBS notes provide a comprehensive approach to diabetes management for NEET PG and USMLE.