Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that accelerates the growth cycle of skin cells, leading to thick, red, scaly patches. Understanding its pathophysiology, types, and treatment options is vital for medical students.
Pathophysiology
- An autoimmune response triggers rapid skin cell production.
- Inflammatory cytokines play a significant role in disease progression.
Types of Psoriasis
-
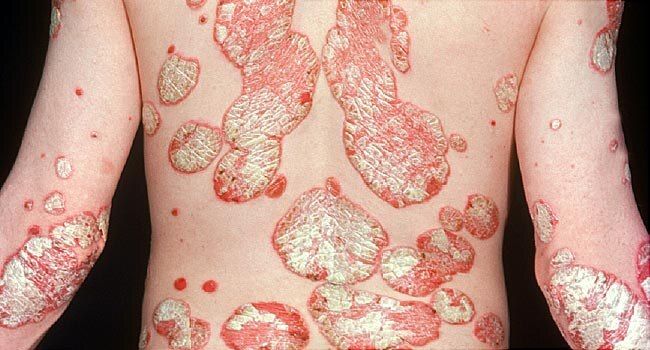
Plaque Psoriasis
- The most common form, characterized by red patches with silvery scales.
-
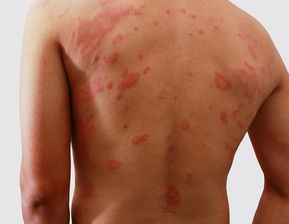
Guttate Psoriasis
- Small, drop-shaped lesions often triggered by bacterial infections.
-
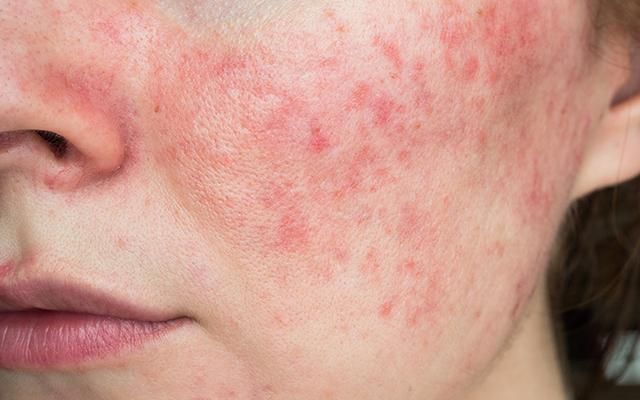
Inverse Psoriasis
- Occurs in skin folds, causing smooth, red lesions.
-
Pustular Psoriasis
- White pustules surrounded by red skin.
Treatment Options
- Topical treatments: Corticosteroids, vitamin D analogues.
- Phototherapy: UVB or PUVA treatments.
- Systemic treatments: Methotrexate, cyclosporine, biologics.
Conclusion
Understanding psoriasis's pathophysiology and management is crucial for medical practitioners to provide effective care and improve patients' quality of life.