Basic Concepts: Electrophysiology refers to the study of the electrical properties and activities of biological cells and tissues. In the context of the heart, it involves understanding how electrical signals are generated and propagated to regulate heartbeats. These electrical signals originate from specialized cells and travel through a specific pathway to coordinate the heart's contractions.
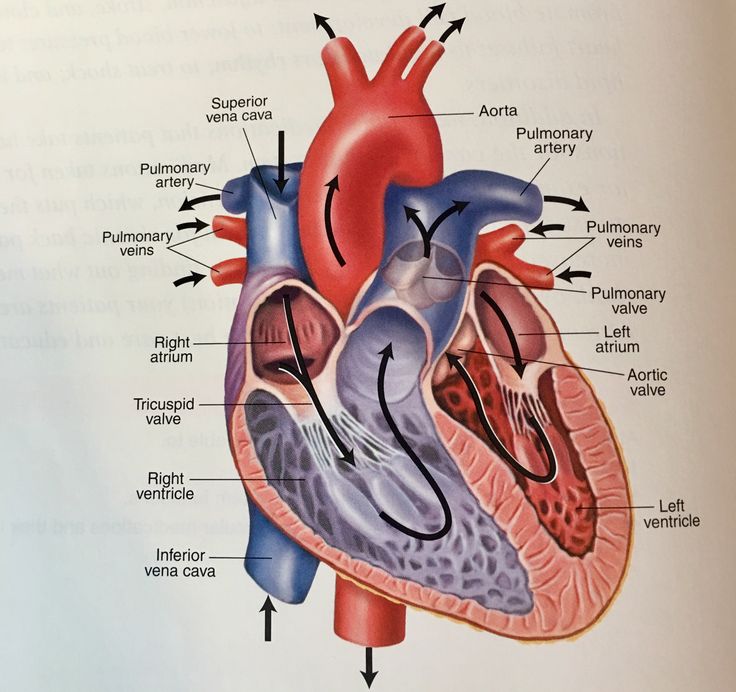
The Heart's Electrical Pathway: The heart's electrical system comprises several key components:
- Sinoatrial (SA) Node: Often called the heart's natural pacemaker, the SA node is located in the right atrium. It generates electrical impulses that initiate each heartbeat.
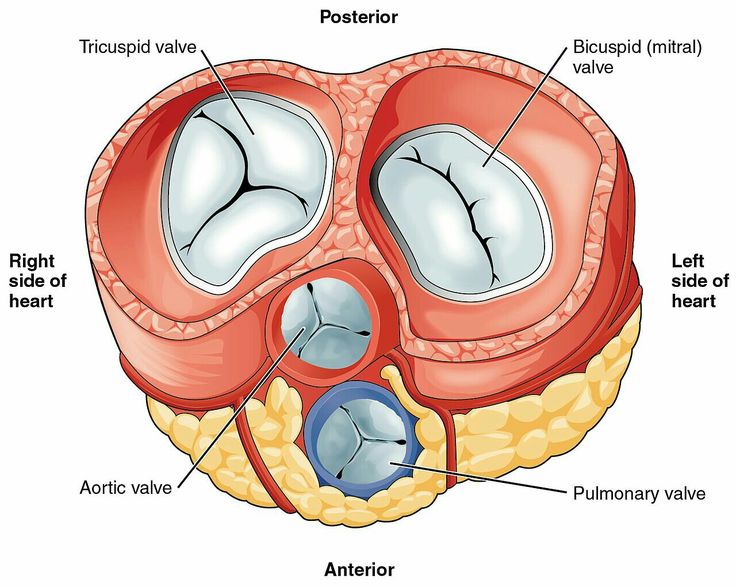
- Atrioventricular (AV) Node: The AV node, located between the atria and ventricles, acts as a gateway, delaying the electrical impulse before it passes to the ventricles. This delay ensures that the atria contract first, filling the ventricles with blood before they contract.
- Bundle of His: This bundle of specialized fibers carries the electrical impulses from the AV node to the ventricles.
- Purkinje Fibers: These fibers distribute the electrical impulse throughout the ventricles, causing them to contract and pump blood to the lungs and the rest of the body.
Common Electrophysiological Issues: Various conditions can disrupt the heart's electrical system, leading to arrhythmias, or abnormal heart rhythms. Some common issues include:
- Atrial Fibrillation: Rapid and irregular beating of the atria, which can lead to poor blood flow and an increased risk of stroke.
- Ventricular Tachycardia: A fast, regular beating of the ventricles, which can be life-threatening if not treated promptly.
- Heart Block: A delay or complete block in the transmission of electrical impulses from the atria to the ventricles, causing a slow or irregular heartbeat.
Diagnosing and Treating Electrical Issues: Diagnosing arrhythmias often involves using an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), which records the heart's electrical activity. Treatment options vary depending on the type and severity of the arrhythmia and may include:
- Medications: To control heart rate and rhythm.
- Pacemakers: Implantable devices that regulate the heartbeat.
- Cardioversion: A procedure to reset the heart's rhythm.
- Ablation: A minimally invasive procedure to destroy the tissue causing the abnormal rhythm.
Conclusion: The heart's electrical system is crucial for maintaining a regular and efficient heartbeat. Understanding electrophysiology helps in diagnosing and treating various heart rhythm disorders, ensuring the heart functions optimally. Regular check-ups and monitoring can help detect and manage these conditions, contributing to better cardiovascular health.