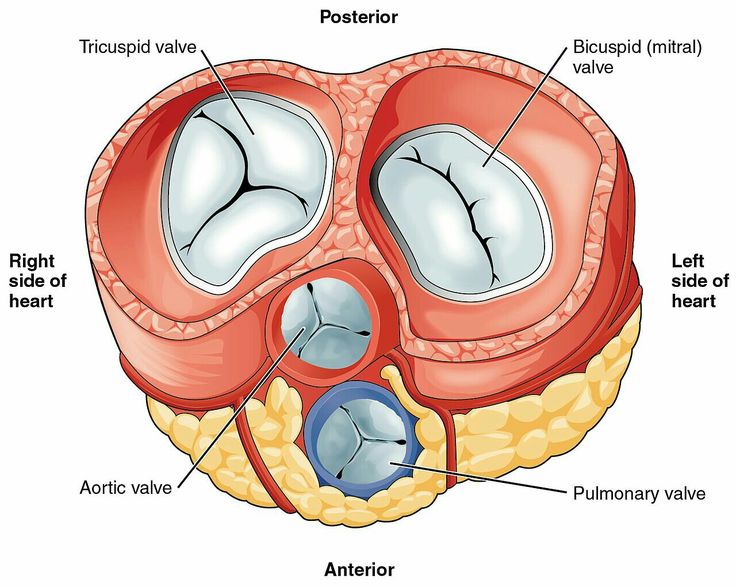
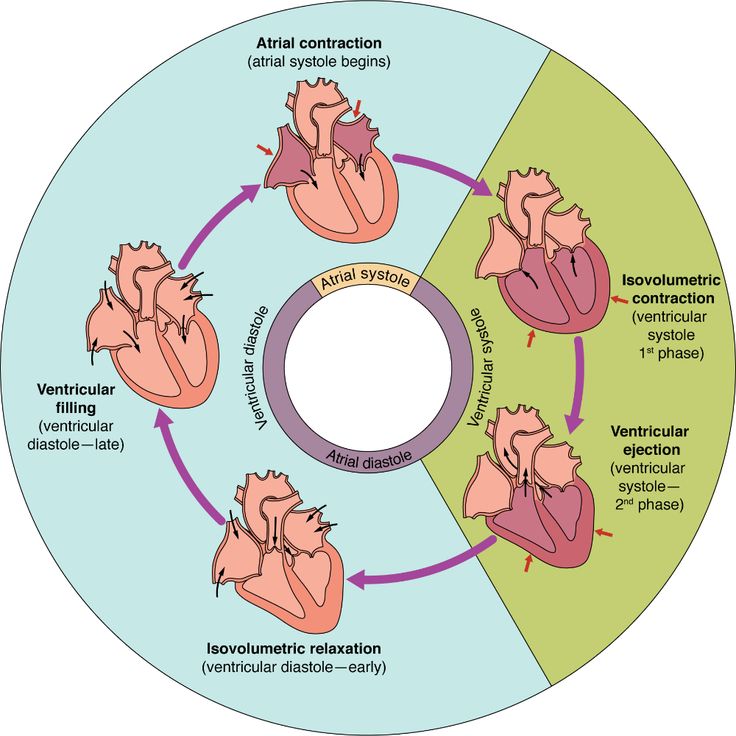
Blood vessels are the essential conduits of the cardiovascular system, responsible for transporting blood throughout the body. Understanding their structure and function is crucial for comprehending how nutrients, oxygen, and waste products are distributed and removed. In this blog post, we will delve into the different types of blood vessels, their roles, and their significance in maintaining overall health.
Types of Blood Vessels: The cardiovascular system consists of three main types of blood vessels:
- Arteries: These vessels carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart to the body's tissues. Arteries have thick, muscular walls to withstand the high pressure of blood being pumped from the heart.
- Veins: Veins return oxygen-depleted blood back to the heart. They have thinner walls than arteries and often contain valves to prevent backflow, ensuring blood moves in one direction towards the heart.
- Capillaries: These are the smallest blood vessels, connecting arteries and veins. Capillaries have thin walls that allow for the exchange of gases, nutrients, and waste products between the blood and surrounding tissues.
Arterial System: The arterial system begins with the aorta, the largest artery in the body, which branches into smaller arteries that extend throughout the body. The structure of arteries includes:
- Elastic Arteries: Such as the aorta, these arteries have a high capacity to stretch and recoil, helping to maintain blood pressure.
- Muscular Arteries: These medium-sized arteries distribute blood to specific organs and regulate blood flow through vasoconstriction and vasodilation.
Venous System: The venous system includes veins that carry blood back to the heart. The key features of veins include:
- Superficial Veins: Located close to the skin, these veins are often visible and help in temperature regulation.
- Deep Veins: Located deeper within the body, these veins carry the bulk of the blood back to the heart and often run parallel to arteries.
Capillary Network: Capillaries form extensive networks within tissues, allowing for efficient exchange of materials. Their thin walls, composed of a single layer of endothelial cells, facilitate the diffusion of oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, and waste products.
Blood vessels are crucial components of the cardiovascular system, ensuring the efficient transport of blood, nutrients, and waste products throughout the body. Understanding their structure and function is fundamental for medical students and professionals. Regular cardiovascular health check-ups and a healthy lifestyle can help maintain the integrity and function of these vital pathways.