Bone marrow plays a crucial role in hematology as the primary site for new blood cell production, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. This post will explore the function of bone marrow, its role in various hematologic disorders, and its importance in treatments like bone marrow transplants.
Body:
-
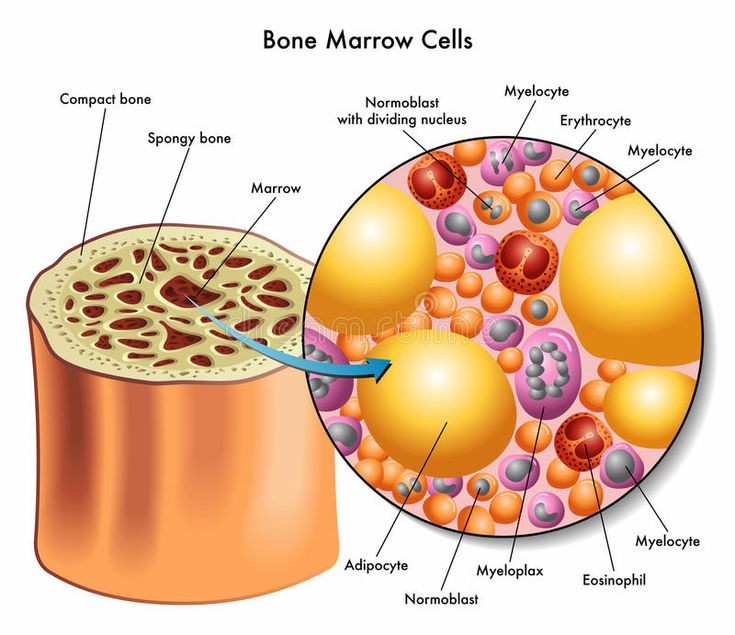
Function of Bone Marrow:
- Hematopoiesis: The process of blood cell production, taking place in the bone marrow.
- Stem Cells: The origin of all blood cells, which differentiate into various types of blood cells.
- Regulation: How the body regulates the production of blood cells based on its needs.
-
Bone Marrow Disorders:
- Aplastic Anemia: Failure of the bone marrow to produce sufficient blood cells.
- Leukemia: Abnormal production of white blood cells in the bone marrow.
- Myelodysplastic Syndromes: A group of disorders caused by poorly formed or dysfunctional blood cells.
-
Bone Marrow Transplants:
- Types: Autologous (using the patient’s own cells) and allogeneic (using a donor’s cells).
- Procedure: How bone marrow transplants are performed and their role in treating various hematologic conditions.
- Risks and Benefits: Potential complications and the life-saving benefits of bone marrow transplants.
Conclusion: The bone marrow is a vital organ in the field of hematology, and understanding its function is crucial for medical students. This post provides essential insights into how bone marrow works and its role in both disease and treatment.