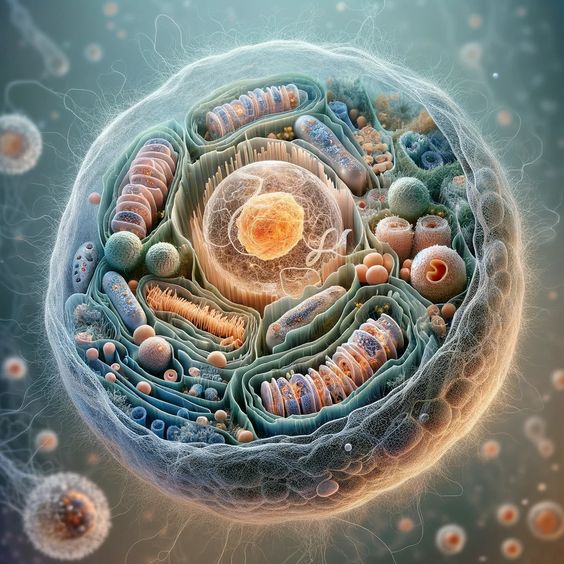
The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a crucial component of cell structure. It acts as a barrier, controlling the movement of substances in and out of the cell, and plays a vital role in maintaining the cell's integrity and communication with its environment.
Structure of the Cell Membrane
The cell membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins, cholesterol, and carbohydrates. The hydrophobic tails of the phospholipids face inward, while the hydrophilic heads face outward, creating a semi-permeable barrier.
Functions of the Cell Membrane
- Selective Permeability: Controls what enters and exits the cell.
- Communication: Contains receptors for signaling molecules.
- Protection: Provides a boundary to protect cellular components.
- Support: Maintains cell shape and supports the cytoskeleton.
Conclusion
Understanding the cell membrane's structure and function is fundamental for medical students, as it is essential for many cellular processes and overall cell health.