Blood pressure regulation is a complex process that ensures adequate blood flow to organs and tissues. Maintaining optimal blood pressure is crucial for overall health and preventing cardiovascular diseases. In this blog post, we will explore the mechanisms involved in regulating blood pressure, including neural, hormonal, and renal controls.
Neural Control:
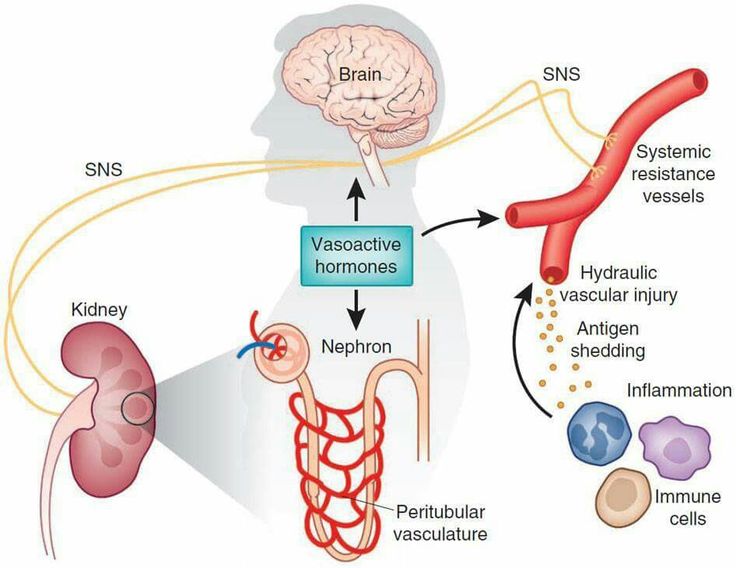
- Baroreceptors: These pressure-sensitive receptors located in the carotid sinuses and aortic arch detect changes in blood pressure. They send signals to the cardiovascular center in the brainstem to adjust heart rate and vascular tone.
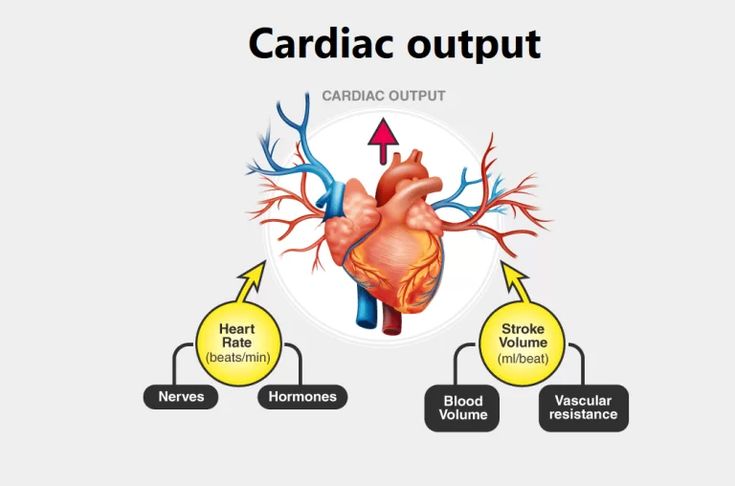
- Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Nervous Systems: The sympathetic nervous system increases heart rate and vasoconstriction, raising blood pressure. The parasympathetic nervous system lowers heart rate and promotes vasodilation, reducing blood pressure.
Hormonal Control:
- Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS): This system regulates blood pressure by controlling blood volume and systemic vascular resistance. Renin release from the kidneys triggers a cascade leading to angiotensin II production, causing vasoconstriction and aldosterone release, which increases blood volume.
- Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH): ADH, also known as vasopressin, promotes water retention in the kidneys, increasing blood volume and pressure.
- Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP): Released from the atria in response to increased blood volume, ANP promotes vasodilation and increases urine output, reducing blood pressure.
Renal Control:
- Direct Mechanism: The kidneys regulate blood pressure by adjusting blood volume. Increased blood pressure leads to increased urine output, reducing blood volume and pressure.
- Indirect Mechanism: The RAAS system, as previously mentioned, also plays a role in renal control of blood pressure.
Clinical Implications:
- Hypertension: Chronic high blood pressure can lead to various health issues, including heart disease, stroke, and kidney damage. Understanding blood pressure regulation helps in managing hypertension effectively.
- Hypotension: Abnormally low blood pressure can cause dizziness, fainting, and inadequate blood flow to organs. Identifying the underlying cause is crucial for appropriate treatment.
Blood pressure regulation is a vital process that involves neural, hormonal, and renal mechanisms. Understanding these controls is essential for diagnosing and treating blood pressure-related conditions. Medical students and professionals must have a thorough knowledge of these mechanisms to ensure effective cardiovascular health management.